Libraries Going Digital: A Guide Through Useful Features For Library Websites, and How Drupal Fits In
Authored by: Nadiia Nykolaichuk.
Libraries are known as one of the most traditional ways of helping people get valuable knowledge. Most people imagine a library as a quiet building with long shelves, filled with the scent of well-worn books and the quiet rustle of turning pages. It’s a true intellectual haven, and librarians are its guardians.
What about the modern digital world where so much content can be found in a mere click? Does it diminish the importance and popularity of libraries? Fortunately, libraries have adapted to the changing habits of society. In addition to being physical intellectual havens, many libraries are successfully becoming digital intellectual havens as well. That’s because a great number of library services can be effortlessly extended into the online domain. Let’s take a look at how this can all be implemented on a library website.
A guide through the features that make a great library website, and how Drupal helps
Libraries VS. an ocean of online resources: how to stand out?
The abundance of readily available content across the web is both a blessing and a challenge for knowledge seekers. They need to dig out the trustworthy, high-quality information. One of the best ways to do that is to rely on a respected source such as a library.
In these circumstances, a library website has the role of enhancing the library’s visibility, reputation, and brand identity online. And, of course, the mission of digitizing a library’s services, in every technical detail, lies on a website’s “shoulders.”
Given the above, a library needs a robust and reliable website built with an enterprise-level platform. Therefore, the Drupal CMS looks like a solid choice. It has unlimited options for creating website functionalities, so whatever library services you’d like to digitalize, you can.
Drupal is a free, open-source CMS with a modular structure. In addition to the Drupal core (the out-of-the-box suite of the most essential modules for a website), there are thousands of free community-contributed modules for various features, which speed up the setup through the user interface and mostly require no coding. Custom coding is used for special website requirements, and it is based on best practices in Drupal.
When it comes to enhancing a library’s brand identity, Drupal is a great choice because it is not a simplistic DIY kit with standard, unchanging templates for everyone. On the contrary, Drupal offers unlimited design options to make your library website unique from header to footer. Drupal’s theming system allows for the creation of custom-branded library websites, tailored to match the library’s aesthetics. Drupal keeps adopting the most modern technologies for themers, one of the latest examples being Single Directory Components for quick and effective creation of your library’s visual interface.
Presenting content online
An important part of digitizing a library is presenting its resources online. There are two main options for libraries to do this, and usually, they combine them both:
- A library website can display the resources that users can borrow from a physical library. This approach creates a digital catalog or index, making it easier for users to discover materials. The information about each piece may include titles, authors, publication dates, image covers, and more. Users might be allowed to make reservations and see the availability of resources.
- Some content can be available online in full. This might include audiobooks, e-books, digital newspapers, podcasts, video lectures, webinars, scanned historical maps, documents, photographs, and more.
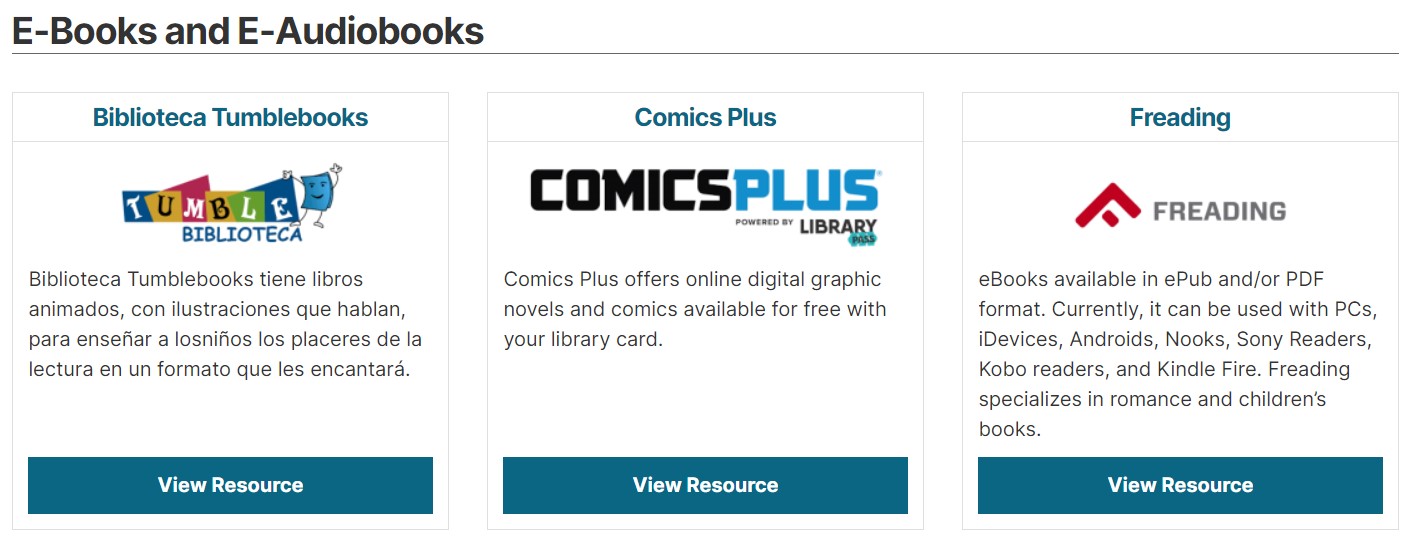
When it comes to handling a great variety of online materials, a strong content management system is a true salvation. The Drupal CMS has consistent content types and media types to present any of your library’s content. Each content type or media type has a configurable field-based structure, and it’s easy for editors to add content items of a specific type. Drupal’s built-in media types such as Audio, Video, Remote video, Document, and Image might be especially useful for libraries.
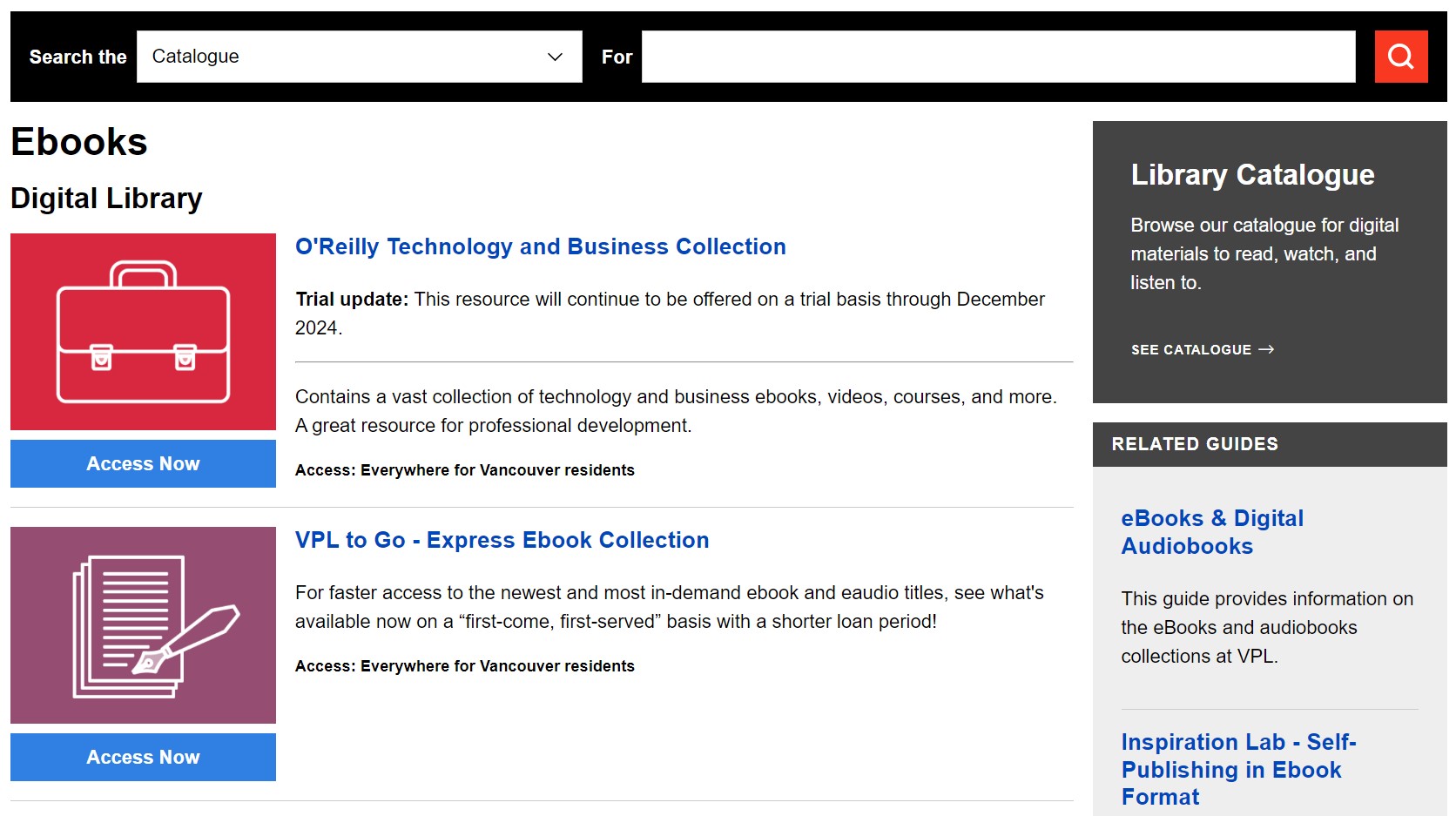
Library catalog pages, featured collections, or thematic displays can be presented based on specific criteria as customizable grids, lists, or tables with the help of built-in Drupal Views.

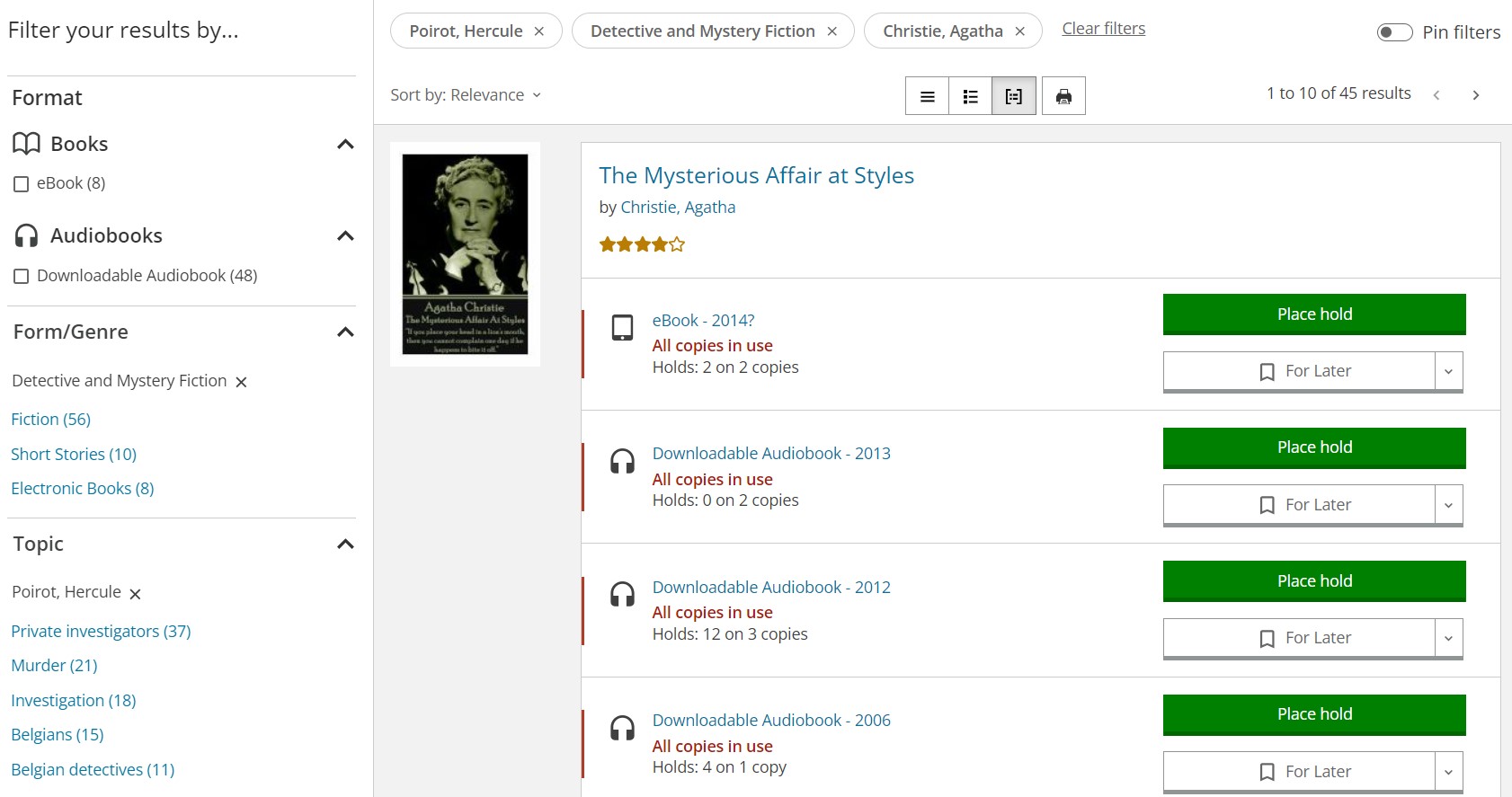
Proper categorization and search
In all the abundance of materials, users need to be able to quickly find the library resources they are looking for. In a physical library, the materials are commonly organized by format, subject, genre, author, and so on. Luckily, digital content organization is much easier than the physical equivalent.
The robust built-in Drupal taxonomy system is one of the most essential solutions for libraries. It helps online library managers organize content into categories and subcategories by adding tags. Once content is tagged, a great number of taxonomy-based setups are possible, for example, displaying collections of content with Drupal Views based on its genre, subject, author, etc.
Views offer powerful filtering and sorting capabilities that can be exposed to users for their most efficient content research. They can be based on taxonomy and many other criteria. For example, users can choose to sort the materials from newest to oldest, filter by the specific author, reading level, and so on.
Furthermore, Drupal has powerful contributed modules available for building customizable search interfaces such as Search API, Search Autocomplete, Facets, Apache Solr Search, Elasticsearch Connector, and more. You can use databases or third-party search services as a source of data. Your library website users can enjoy advanced search features like faceted search, fuzzy search, stem search, autocomplete, results sorted by relevance, and more.
User management and access
The next thing to discuss in this guide is that library website users need their own accounts to access some of the library’s services.There also needs to be different levels of access to website content and administrative functions based on roles. The roles might include Librarian/Staff member, Member, Premium member (with access to subscription content), Content contributor, Event coordinator, and Digital archivist, to name a few.
Drupal has user account functionality and a comprehensive system of roles and permissions. Many flexible settings for user access can be provided through the built-in capabilities and add-on contributed modules.
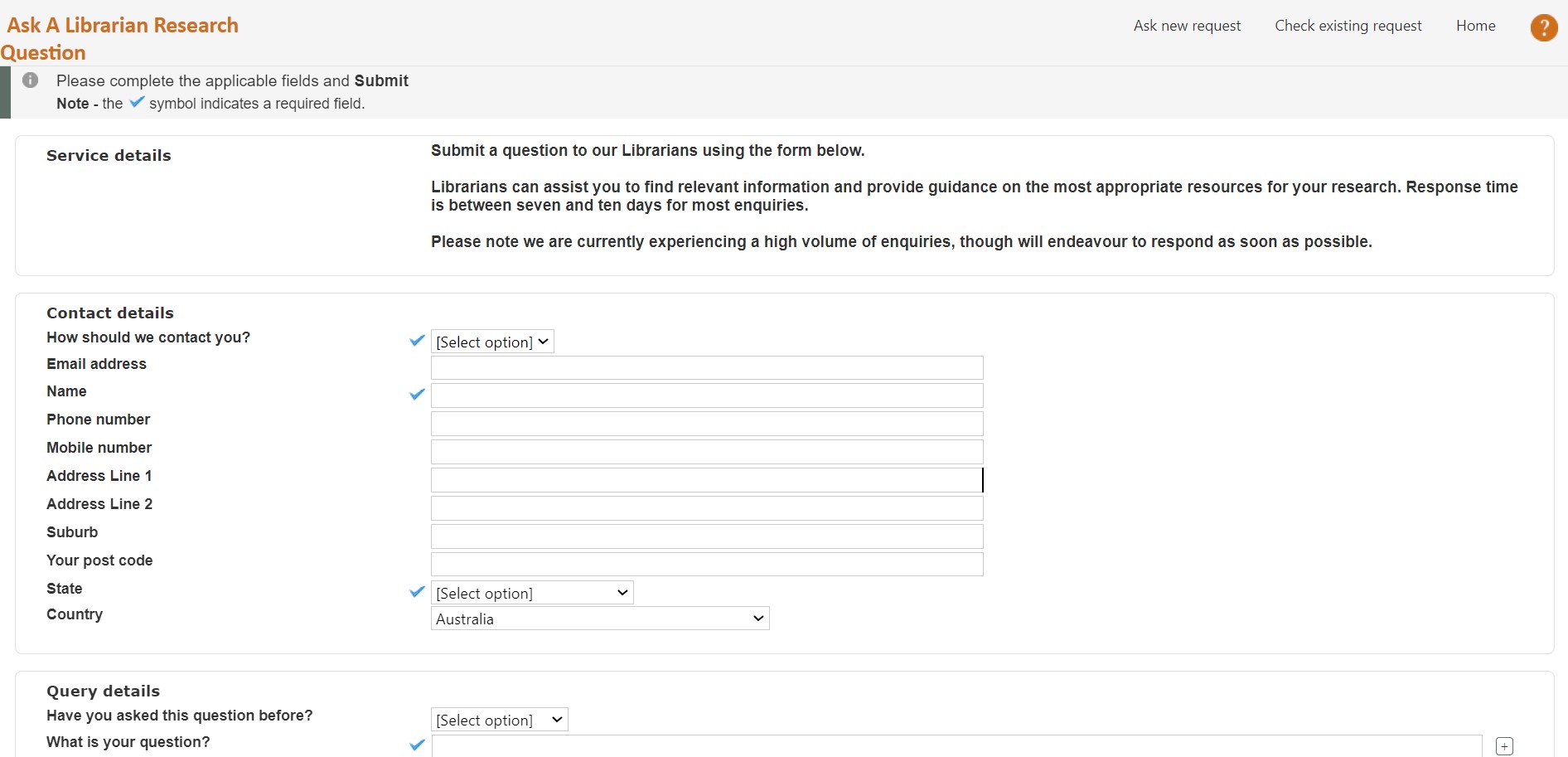
Virtual reference services and online consultation
It’s not only in a physical library that visitors can request a librarian’s help. Library websites can provide virtual reference services, such as online chat and email reference, which allow users to get help with their research from anywhere.
Well fortunately Drupal covers that! For establishing online communication forms, Drupal developers can use the Form API, but the functionality can also be more easily created via a UI thanks to an extremely feature-rich Webform module. Email notifications, file uploads, spam protection, pre-population, customizable results view, and submission analysis are just a few examples of the endless list of possible features of Webform. With Drupal, it’s also easy to add an online chat in just a few steps.
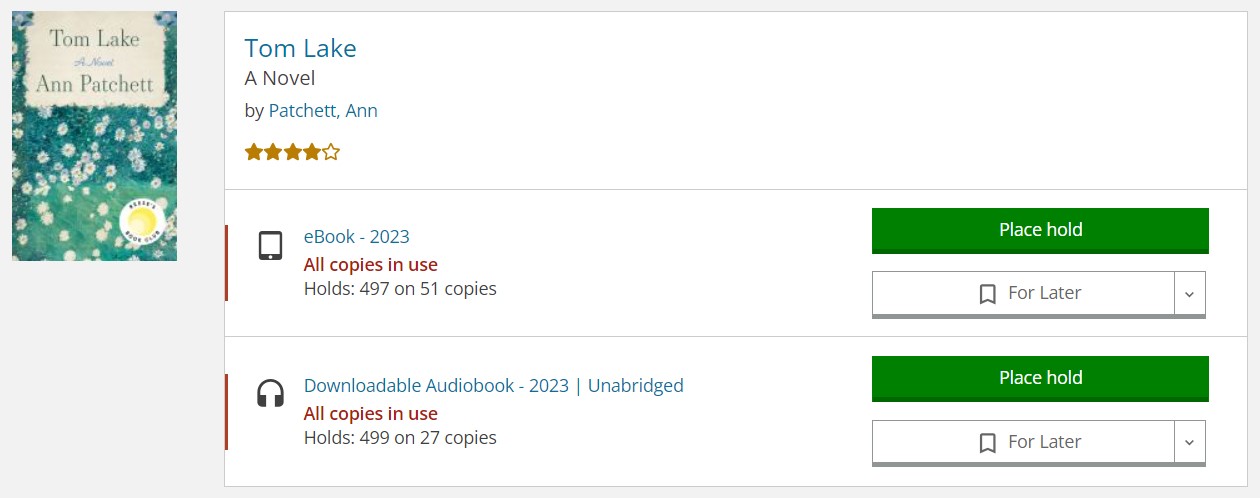
Resource management and online reservations of materials
Library websites often need integration with library management systems for real-time updates on inventory, or digital resource management of the content materials. A library website might also provide a reservation system for placing holds on items and the capability for users to renew borrowed items online.
Drupal has an extensive framework for integration with 3rd party APIs, including RESTful APIs that many Library Management Systems (and other systems libraries often use) provide. This integration might give you real-time updates on inventory, including information on available copies, checked-out items, new acquisitions, user account integration, real-time notifications, and other features.
An abundance of Drupal tools might be very helpful for online reservations such as user accounts, user roles and permissions, the Webform module or the core Form API to create online forms for users to request renewals and place holds, the Rules module to trigger reminders about returning the borrowed books, and so on.
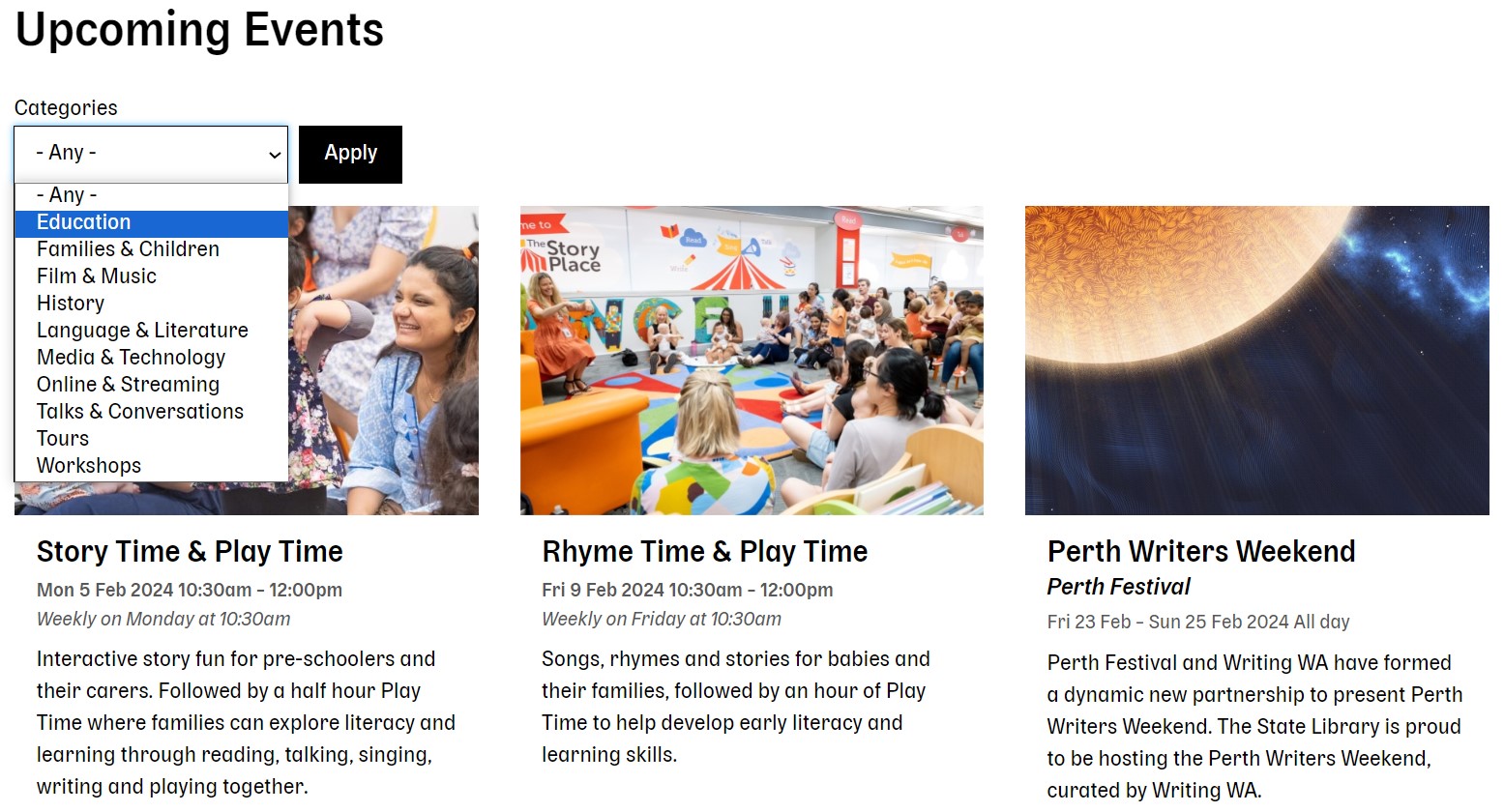
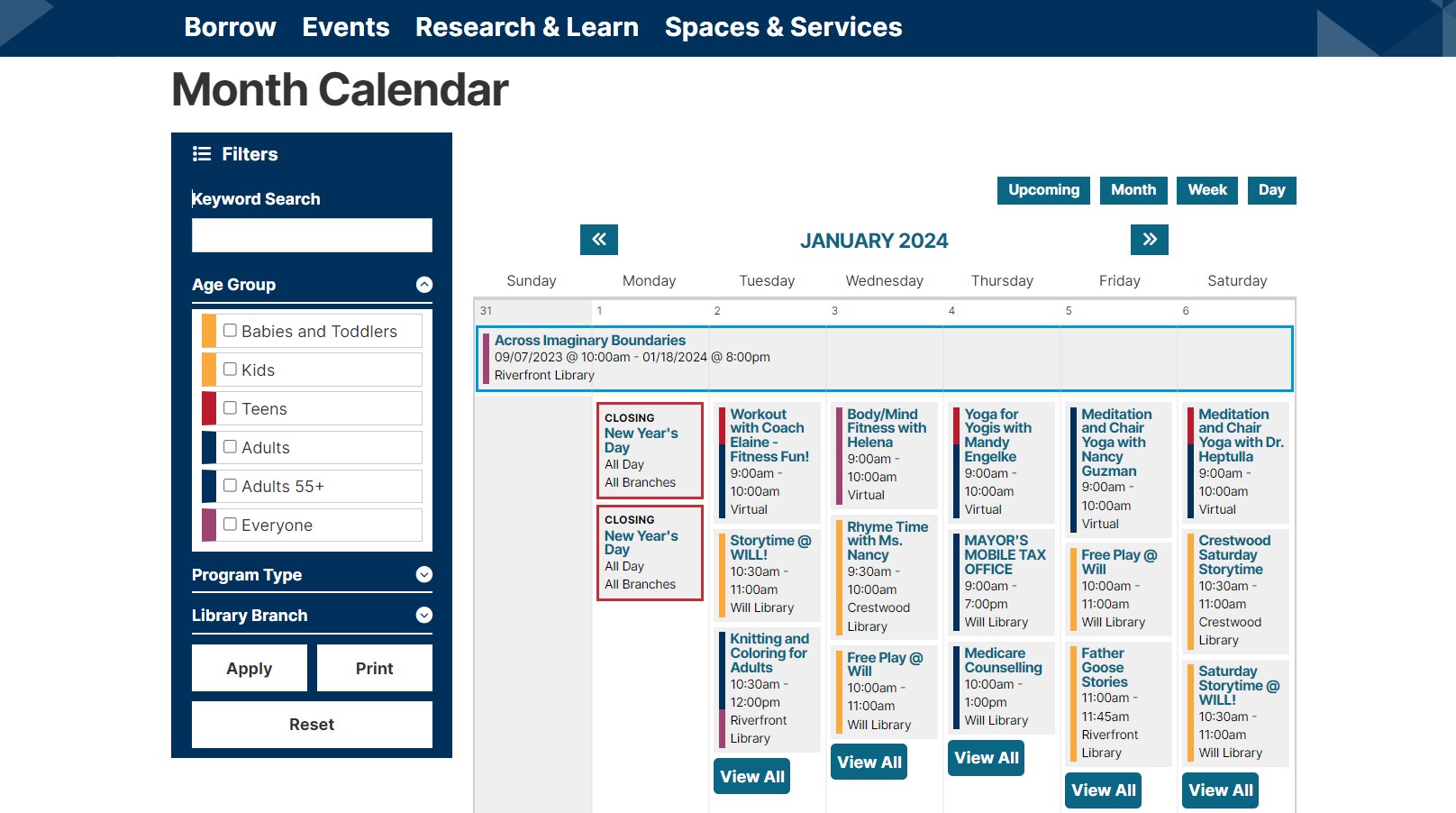
Library events
Libraries often organize and promote events, such as book clubs, author talks, workshops, or lectures. It’s great to display an event calendar on a library website, as well as provide online registration. In addition to just announcing events, a library website can host events virtually.
Drupal’s arsenal of tools for event features is huge. It’s possible to create events as content types and display them in the most appealing way using traditional Views or calendar-specific modules like Calendar View or Fullcalendar View. Modules like Smart Date can handle even the most intricate date and time settings, the Webform module or the core Form API are perfect for online registrations, streaming from third-party video services is seamless with Drupal’s Media system, and the list of possible options could go on.
Sales or digital lending of content products
Content with high production costs might need to be bought or rented by library users:
- Ways to buy include direct purchase and PDA (Patron Driven Acquisition) — a model for acquiring books and other library materials based on actual demand from patrons or users.
- Libraries can offer digital lending of content that can be borrowed remotely. The digital lending of books on a library website can be either paid (a membership-based or a pay-per-use model) or free.
Implementing purchase, Patron Driven Acquisition (PDA), and digital lending of books involves leveraging various modules, configurations, and potentially integrating third-party services, but any approach is implementable with Drupal.
For direct purchases that involve standard e-commerce transactions, Drupal Commerce is a perfect solution. It has robust features for managing product catalogs, and offers a flexible shopping cart system and checkout workflows. It includes features for inventory management, order fulfillment, stock tracking, and more. Drupal Commerce integrates with various payment gateways, allowing for secure online transactions.
PDA (Patron Driven Acquisition) involves specialized workflows tailored to library practices, such as, for example, automated acquisition triggers based on user interactions. It also often deals with complex licensing agreements and acquisition models. So the implementation would require focusing on:
- creating a robust search interface (Drupal modules for search)
- tracking user interactions with digital content (Drupal modules like Google Analytics etc.)
- setting up automated acquisition rules (the Rules module in Drupal)
- integrating a library management system (Drupal’s extensive integration framework)
- and more
Digital lending would require features similar to those in resource management such as integration with a library management system, access control based on user roles or permissions, and more, which Drupal does very well.
Digital learning platforms
It’s not uncommon for academic libraries to integrate with learning management systems (LMS) and other digital learning platforms. They provide students and faculty with access to educational courses, training programs, or other learning content.
When it comes to integrations, we’ve already mentioned that Drupal is a great choice thanks to its RESTful Web Services and an API-first approach. Furthermore, when it comes to learning management systems, there are some ready-to-go modules to facilitate specific integrations such as, for example, Opigno LMS or Anu LMS. But your choice is not limited by them — any other learning management systems can be integrated with your Drupal library website through some customization.
Mobile capabilities
It goes without saying that a library website needs to provide smooth experiences across all devices, be it desktops, mobile phones, or tablets. Drupal follows a mobile-first principle so Drupal websites are created with mobile responsiveness in mind, which means that page layouts are tailored to the screens they are viewed from.
In addition to responsive web design, some libraries ask for a standalone mobile app that provides access to library services. The deal is sealed thanks to Drupal's integration capabilities, especially RESTful Web Services and JSON:API, which provide seamless ways to share data from a Drupal-based library website to a mobile application.

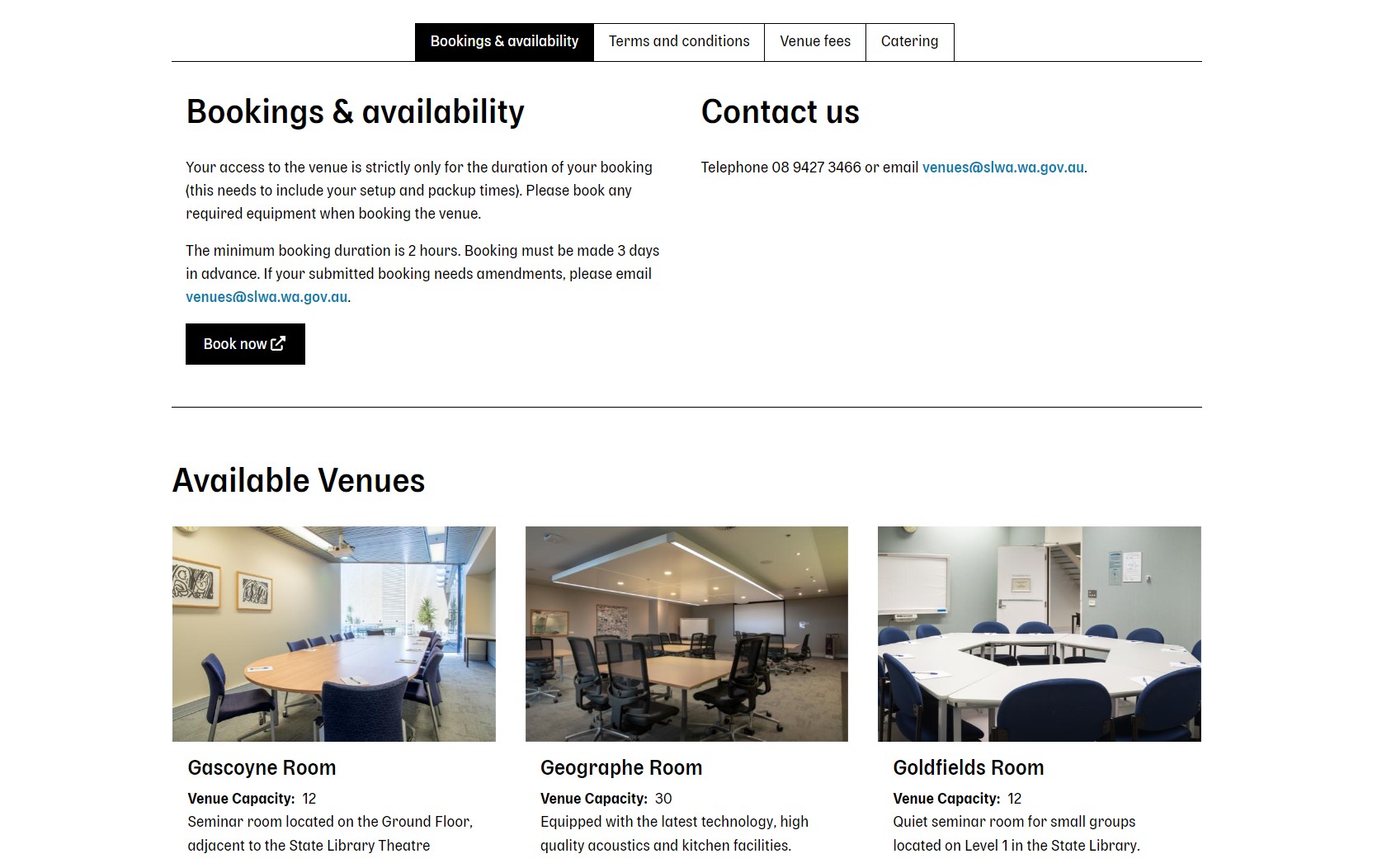
Room or conference hall booking
Many libraries provide room, conference hall, or meeting space booking services. Offering room or conference hall booking is a way for libraries to support community engagement, facilitate learning, and enhance their role as community hubs. Another popular service is computer booking to work in a physical library.
As usual, Drupal comes up with a variety of tools to implement online booking. Its content-type functionality is great for representing the facilities. The Webform contributed module or the core Form API can be used for a booking form. The Rules module might help with creating custom booking rules. Drupal’s core roles and permissions system takes care of access control to manage who can book rooms. Modules like FullCalendar View can enhance the visual representation of room availability. In addition, there are many other options to rely on.
Reaching diverse audiences
One of the reasons libraries go digital is to reach more and more audiences and spread the power of knowledge as wide as possible. To be true ambassadors of learning and culture, they make their websites available to wider audiences.
- The great news is that Drupal adheres to the best accessibility practices to make content accessible to users with disabilities. This includes semantic HTML and WAI-ARIA, required Alt text, keyboard accessibility, and much more.
- Libraries can reach users across the globe thanks to Drupal’s multilingual capabilities. Just out of the box, there is functionality to add multiple languages, configure the specifics of translating the website’s elements and content, and even use ready community-contributed standard interface translation lines.
Evaluation and ratings
You might want to enable users to give star ratings and reviews for the library materials, which can boost engagement and serve as a basis for various collections based on ratings. The implementation will be easy because Drupal has a wealth of contributed modules for evaluation and ratings.
Presence in social networks
Social media presence is essential for retaining a library’s visibility, communicating with users, fostering a sense of community, promoting events, and so much more. Drupal’s wide range of modules for social media integration will make the process a piece of cake.
Wrap-up
In this guide, we have only scratched the surface of how library websites implement useful features with the Drupal CMS. The specific implementations depend on the needs and requirements, and there are always a plethora of options in Drupal. We know that going digital is a huge step for a library, but the right website platform is your ally every step of the way.


