Get Ready for Drupal Canvas, the Page Builder You’ve Been Waiting For
What if building pages in Drupal felt as effortless as sketching ideas on a digital canvas — yet powerful enough to satisfy a developer’s need for precision and control? That’s the promise of Drupal Canvas: a new visual builder that merges the best of what Drupal has offered so far with today’s most modern approaches and best practices.
Drupal Canvas 1.0 was officially released on December 4, 2025. Prepare to be impressed as the tool introduces new ways of building pages, both for non-technical and technical users, that feel intuitive and remarkably advanced.
Canvas was one of the top highlights of Driesnote Vienna 2025, a keynote by Drupal founder Dries Buytaert that traditionally unveils the hottest trends and tools in the Drupal ecosystem. He introduced many new features in Drupal Canvas. The spotlight didn’t stop there, the initiative leads also hosted a dedicated session, offering a deeper look at the tool. Let’s dive in.
What is Drupal Canvas?
Drupal Canvas is a visual, component-based page builder in Drupal CMS that lets you create your entire site right from the browser. It offers multiple ways to build a page: developers can write code using the in-browser editor powered by modern tools, while content creators can add reusable blocks through an intuitive interface — or simply send a prompt to AI and watch the page come to life. You’ll explore all of these approaches (and more) in this article.
Is Drupal Canvas the same as Experience Builder?
You might have heard the name Experience Builder referring to this tool — and yes, Drupal Canvas is its new name. As Dries explained during his keynote in Vienna, there was a trademark issue with the old name. In hindsight, that turned out to be a lucky break: Canvas sounds sleek, elegant, and perfectly fitting for a tool built around creativity and seamless site creation.
Drupal Canvas in Drupal CMS 2.0
Drupal Canvas 1.0 will be part of Drupal CMS 2.0, which should arrive around early January 2026, aligning closely with Drupal’s own birthday, a fitting celebration for this new chapter.
During his keynote, Dries Buytaert noted that Canvas will become the default experience for every new Drupal installation, a shift that, in his words, represents the start of a new chapter for Drupal itself.
Why is Drupal Canvas a big deal?
This question was literally answered by Canvas project leads, Lauri Timmanee and Bálint Kléri. There was a slide at their DrupalCon Vienna session, “Drupal Canvas unleashed: The future of Drupal is here,” that summed up the key points of what makes Canvas so important:
- Canvas unlocks Drupal for the front-end developer community with no need for them to have a deep knowledge of Drupal.
- Thanks to reusable components, projects can be launched faster.
- No-code tools inside Canvas empower non-technical users like content creators.
- The pre-configured AI environment in Canvas helps you start building easily.

What are the latest features in Drupal Canvas for building pages?
Your building foundation: structured components in Canvas
You can start creating your Canvas pages by choosing predefined, reusable components like a hero banner, image gallery, and more. Under the hood, Drupal Canvas relies on the power of Single Directory Components (SDC), a modern approach that keeps all files related to a component in a single folder.
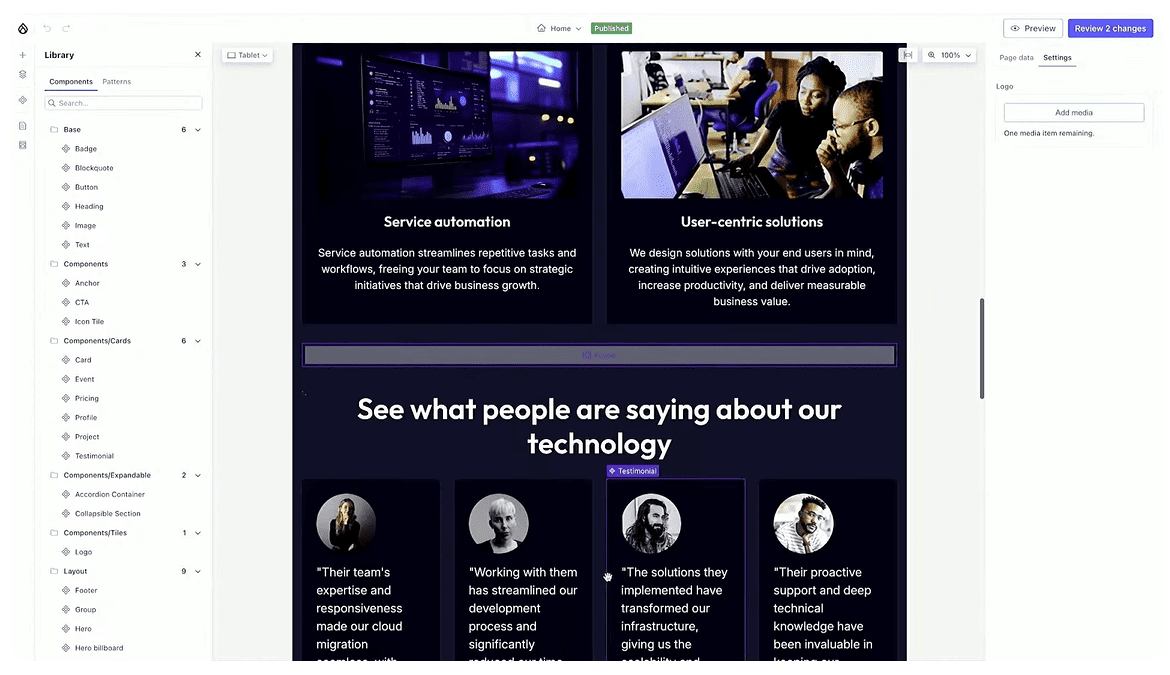
Seamless editing with Drupal’s top modules
As Driesnote demos show, Drupal Canvas makes your page creation process easy and effective thanks to the support for some Drupal core and contributed modules like CKEditor, Metatag, and Webform.
After placing a component, you can now also format text in it, like adding links, changing image alignment, and so on, using the integrated CKEditor.
The Metatag module is also integrated, allowing users to set a meta description and meta image for each page. This ensures that when a page appears in search results or is shared on social media, its preview looks consistent and engaging.
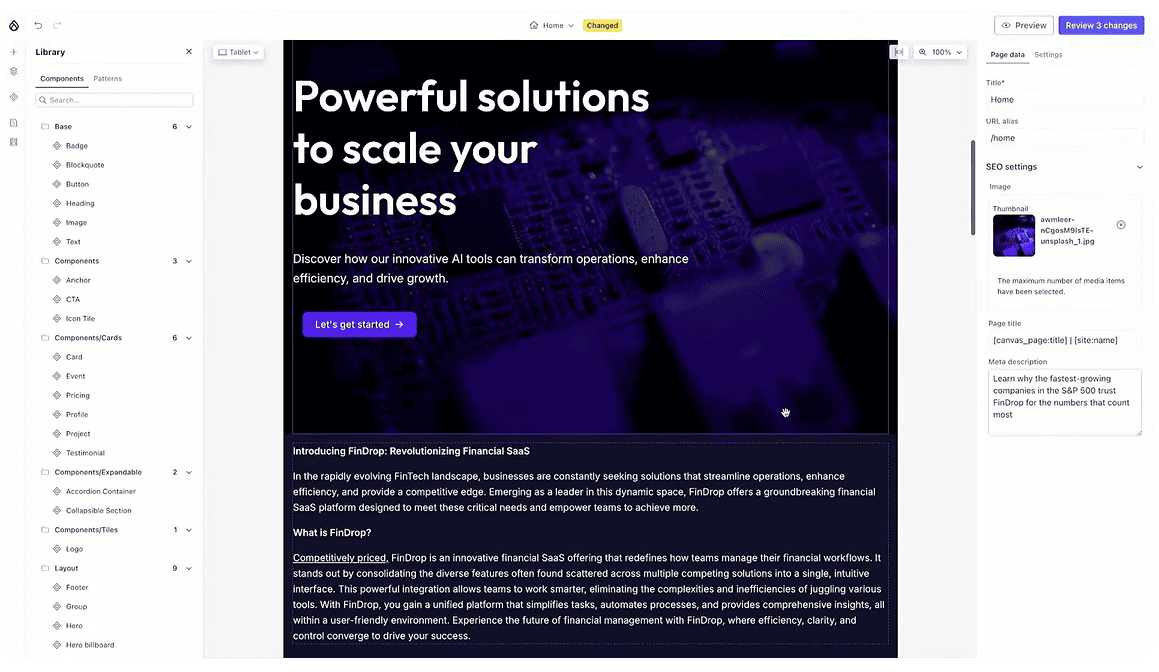
The Webform module is now also Canvas-compatible, so forms can be added as dynamic components right inside Canvas, just like this contact form that we see in the new Mercury theme.
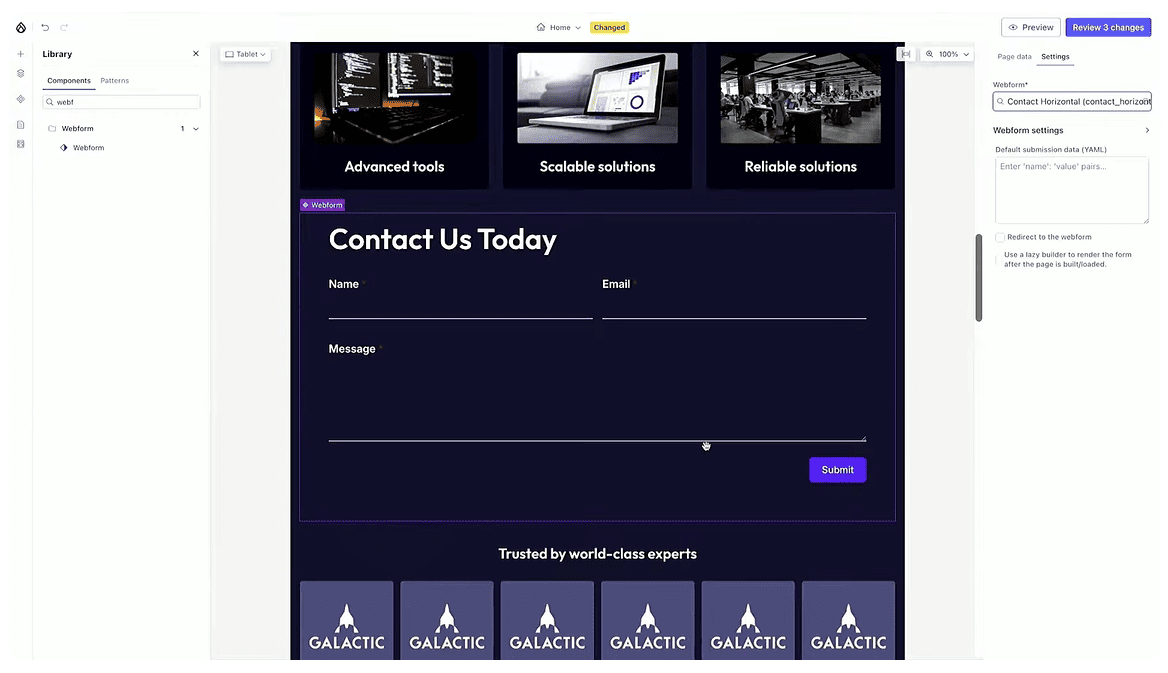
All changes are automatically saved into a workspace, allowing you to review and manage updates before they go live. You can publish all edits at once, or just the selected ones, with a single click.
The next step, according to Dries, is integrating more modules, each one expanding Drupal Canvas’s capabilities and strengthening its connection to the wider Drupal ecosystem.
Using content templates for better layout control in Drupal Canvas
Content templates are a new feature in Canvas that lets you define the look of your content pages in different view modes, all directly in your browser. For instance, the newly introduced site template called “Byte” uses predefined content templates for blog posts.
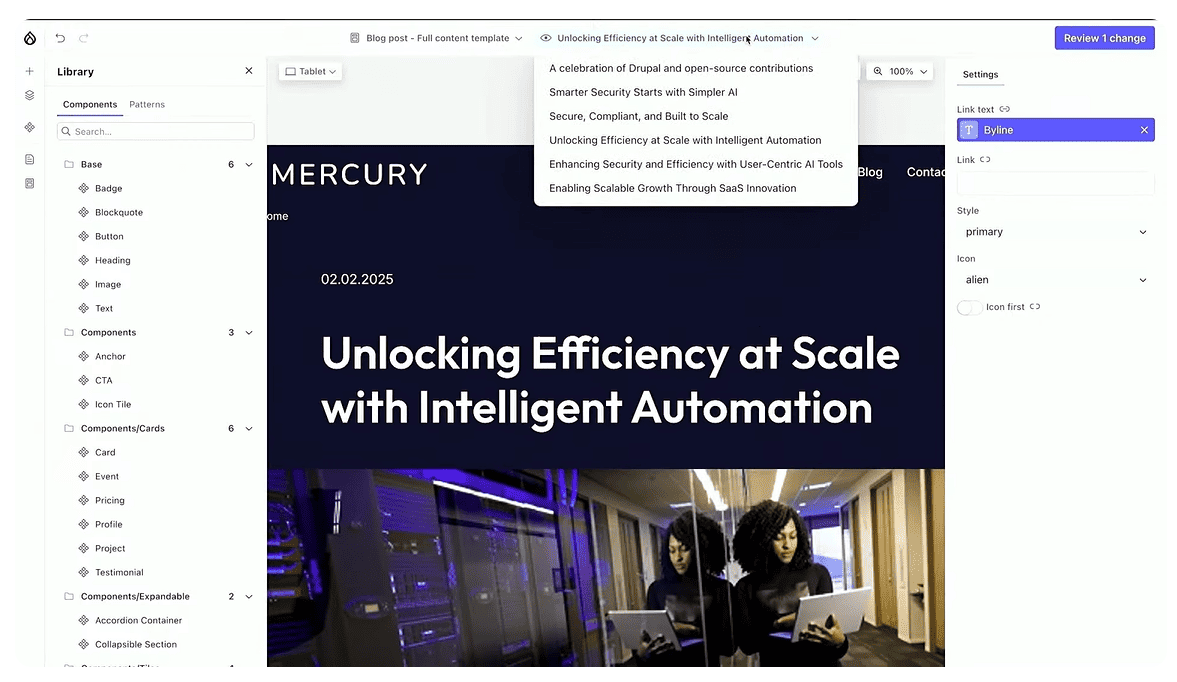
It relies on the Heroblog component to structure the top section of each post — including the title, author name and link, publication date, and more. You can easily enrich these templates by adding any component from the library.
You’ll also see a live preview of content templates populated with real content from your site. You can choose which specific piece of content to use for the preview, making layout editing more realistic. To change a template, you can drag around components and update their properties.
At the session by Lauri and Bálint, we can also see the Destination content template that can be previewed with many exciting destinations.

Code meets design: building custom components in Drupal Canvas
Attention, developers! Drupal Canvas is a powerhouse of modern tools to code your components using the in-browser code editor:
- JSON:API client
Canvas connects to Drupal’s backend through the JSON:API client, which seamlessly retrieves content such as articles, media, and user data using standard API calls. This ensures real-time access to your site’s structured data without additional configuration.
- SWR (stale-while-revalidate)
Developed by Vercel, SWR is a React data-fetching library that keeps Canvas fast and responsive. It displays cached content instantly while quietly updating the data in the background so users always see fresh content without any page reloads.
Drupal Canvas provides debugging information about the response from JSON:API, which supports your coding.
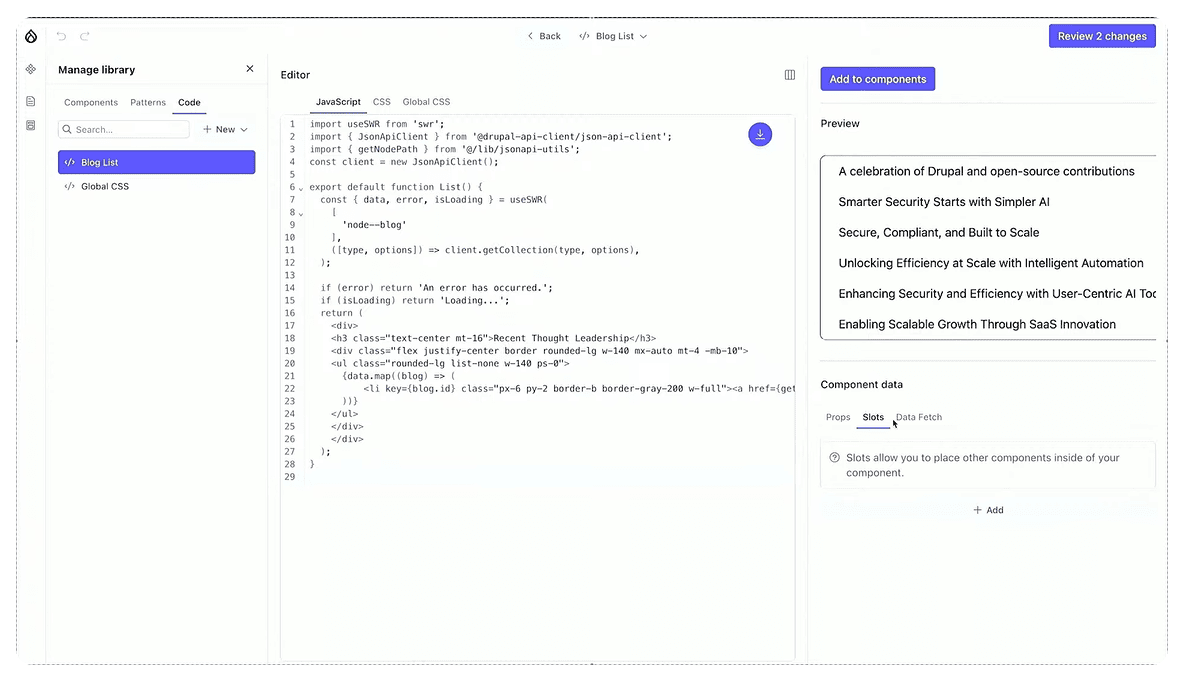
Once you are happy with the component, you can save it to your Library. You can place components on your website where you like at any time.
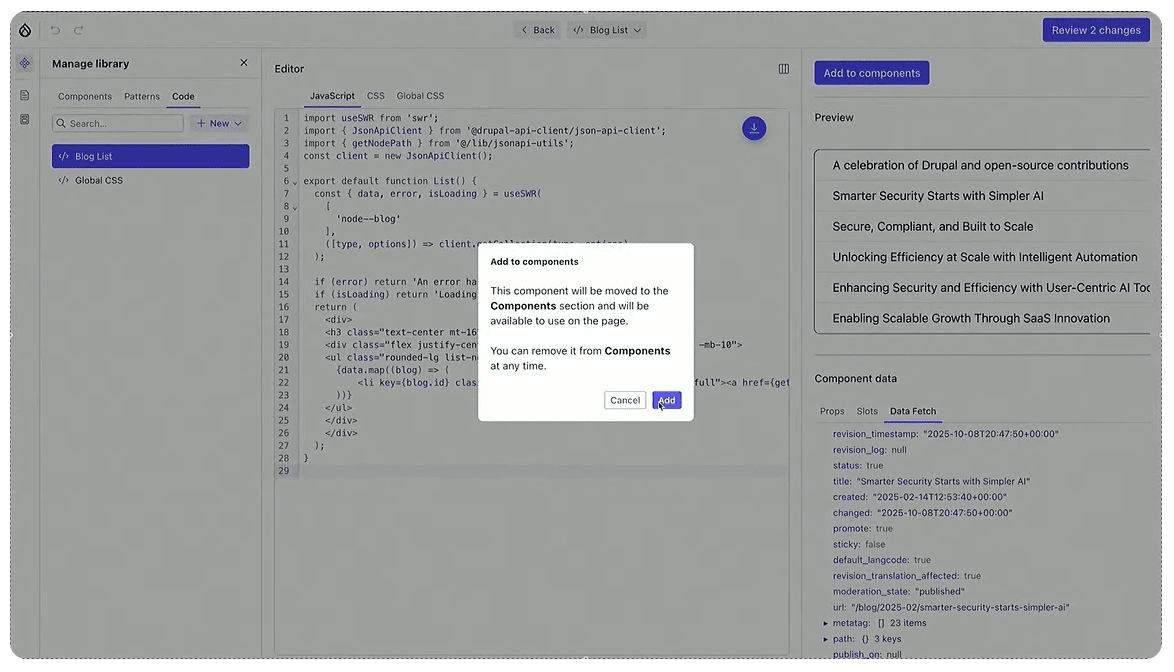
At this Driesnote demo, we see the process of creating a dynamic component without learning any “drupalisms.
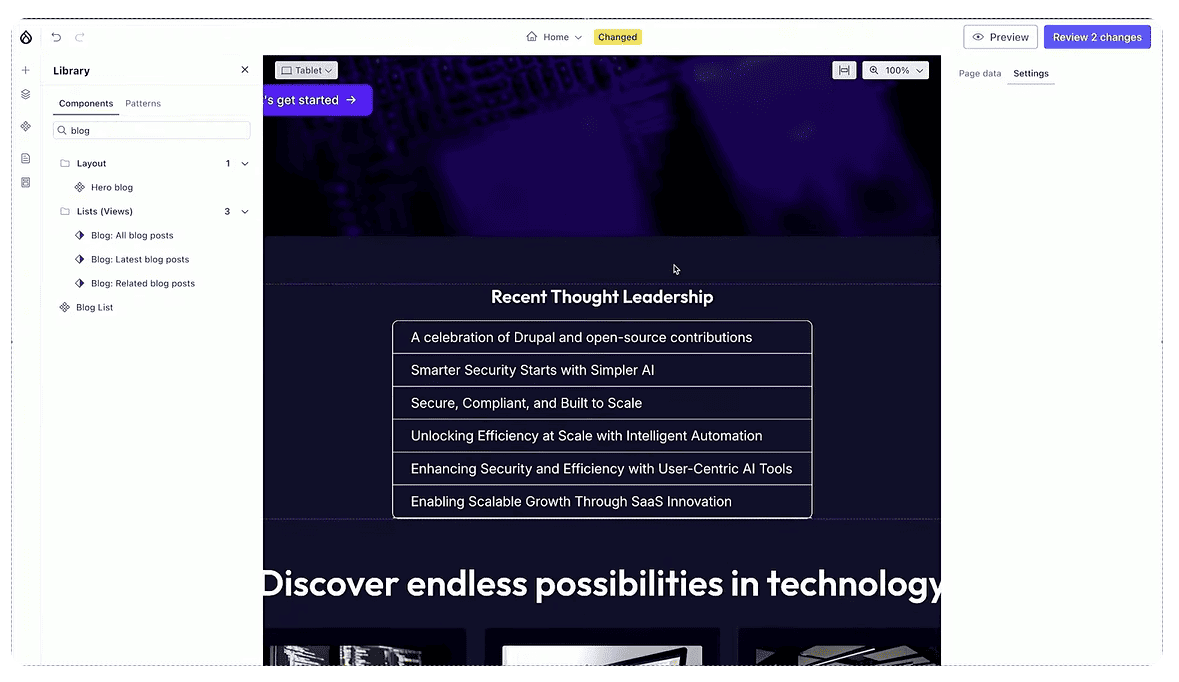
“Props” and “slots”: new concepts in Canvas
As we discover from Lauri and Bálint’s presentation, “props” are the settings to the right of a component that let users change the details title color, background color, and so on. You can define the props when creating your component. “Slots” allow you to place your components inside other components and create component trees where you can drag-and-drop components to change their order.
From Figma to Canvas: auto-creating components without coding
Turning a Figma design into a functional Drupal site has never been a simple task, until now. At Driesnote, we witnessed an exciting breakthrough: a live demo by Witze Van der Straeten showed Drupal and Figma working hand in hand. A pricing table component designed in Figma was instantly generated on a Drupal site, no coding required.
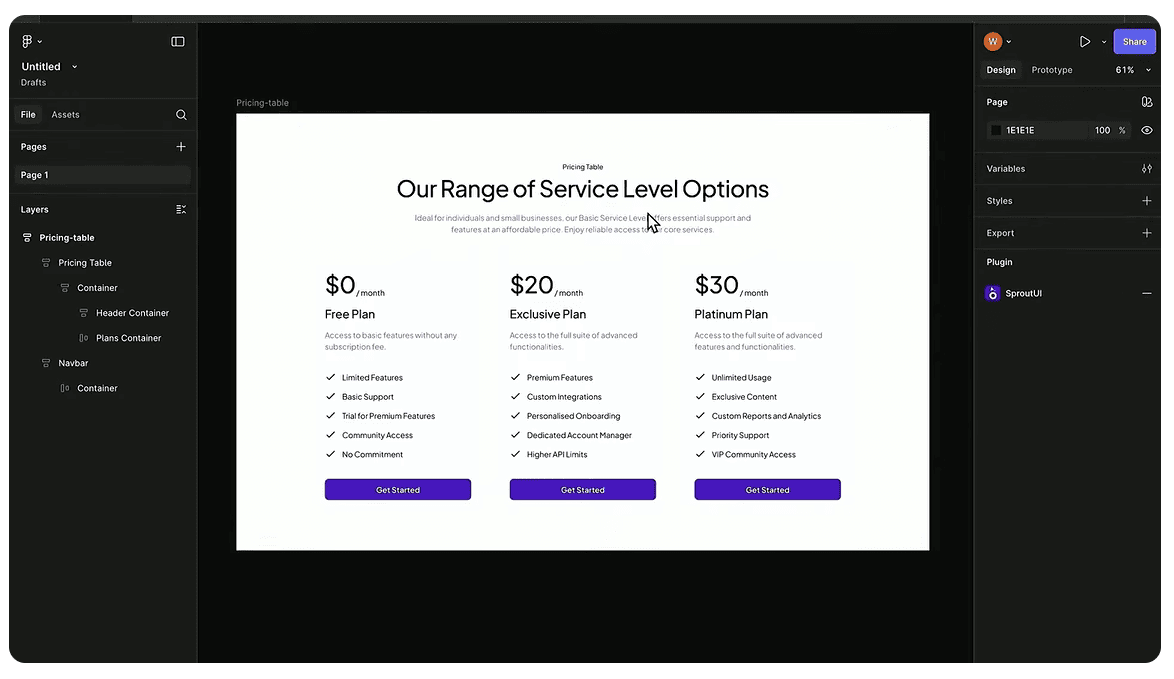
Witze relied on the Figma MCP server, with a bit of assistance from Copilot — his AI coding partner in GitHub. MCP refers to the Model Context Protocol that acts as a bridge between a design system and an AI or code-generation setup.
Here is how it works. You create a new component in Canvas and call it “Pricing table.” A YAML file for this component is created behind the scenes. Copilot then connects to the Figma MCP server, reads the design, and translates its visual structure into Drupal’s component “language.”
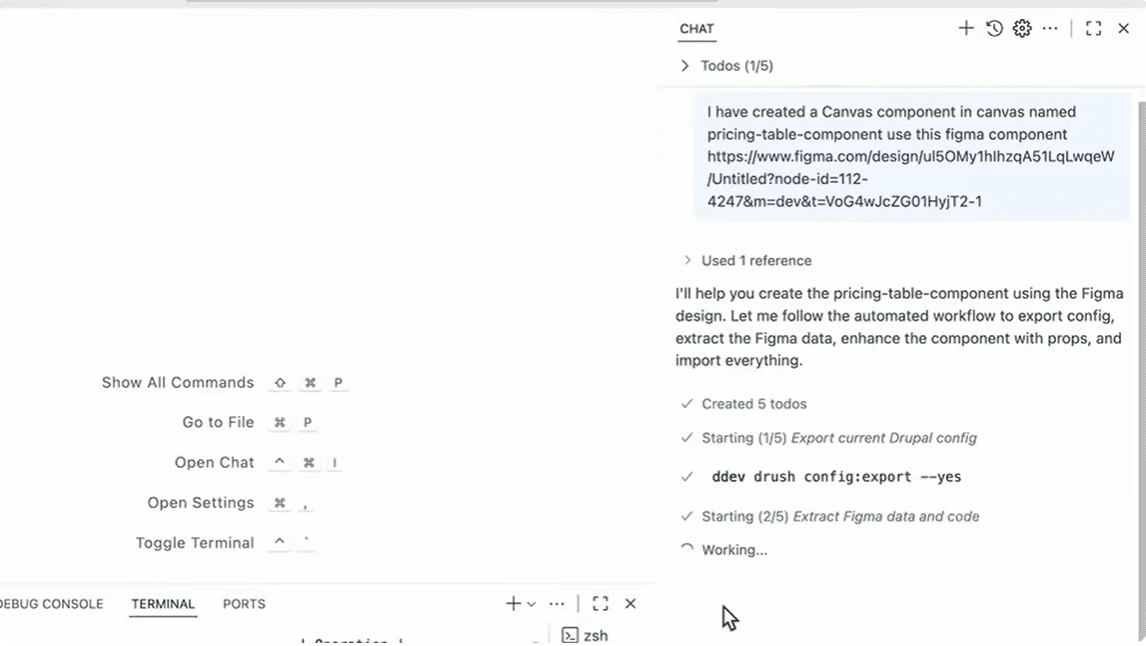
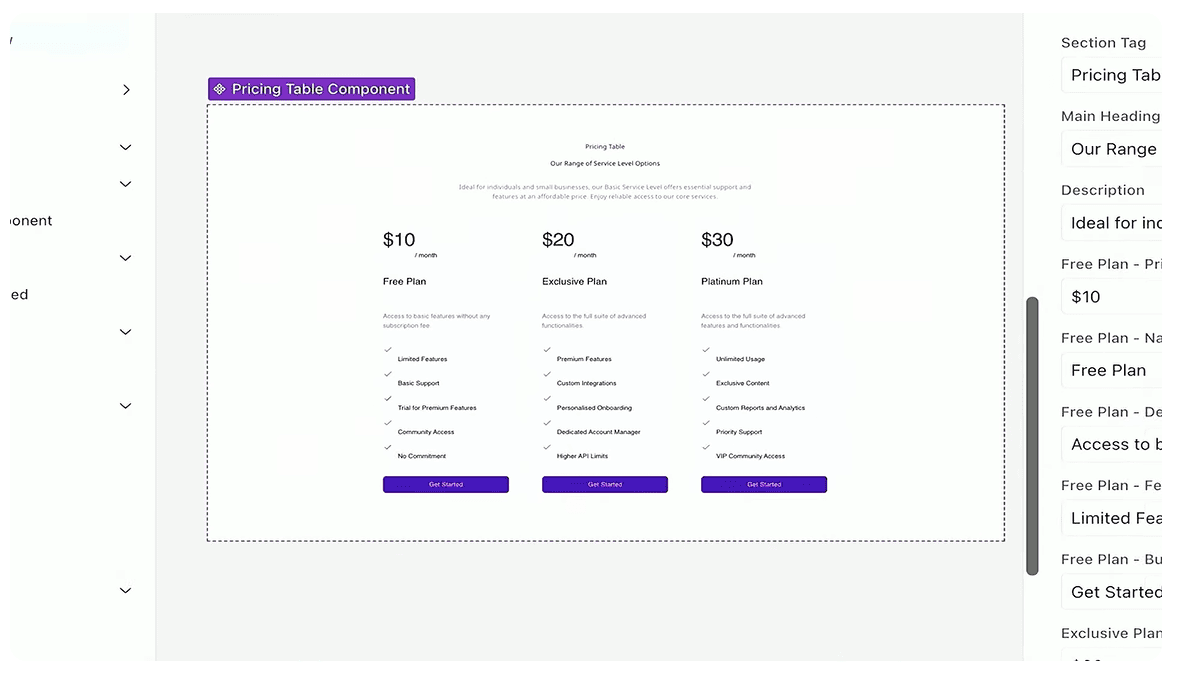
It updates the YAML file, adds responsive field settings, and maps the fields automatically based on the design, but it happens outside of Drupal Canvas. When it’s finished, the YAML configuration is reimported, the cache is rebuilt, and the new component is ready to use.
The pricing table is responsive, editable, and directly based on the Figma design. This used to take hours of manual coding with trial and error, and now it’s handled in seconds.
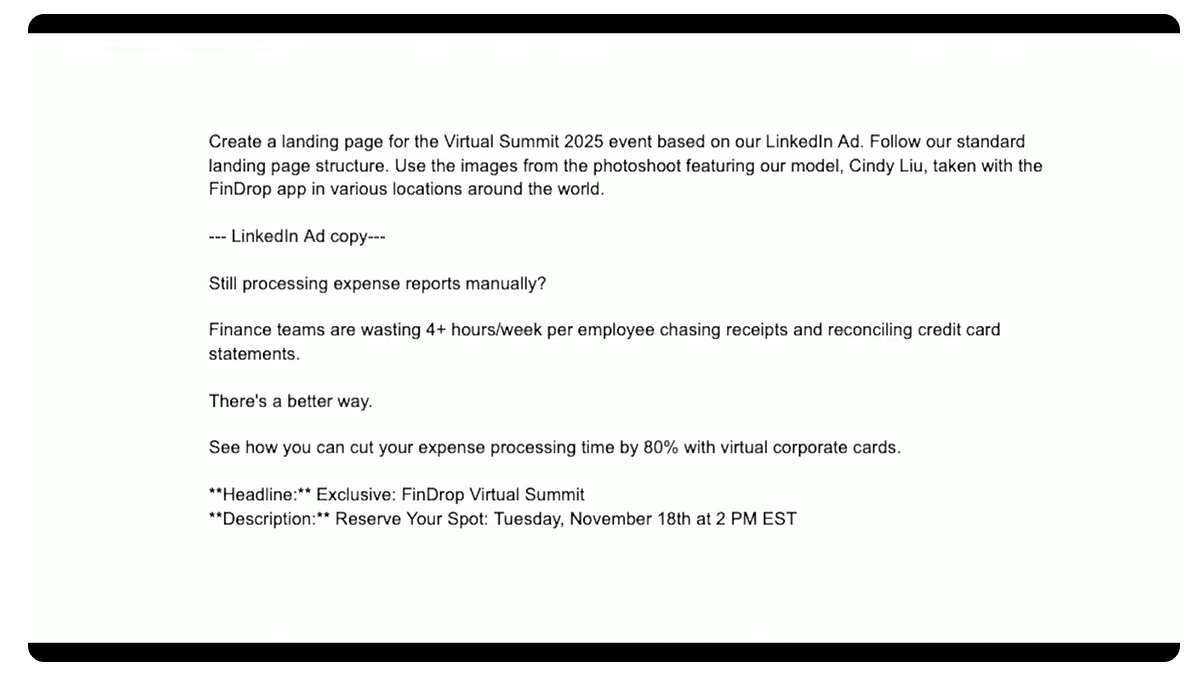
The amazing AI: generating pages in Drupal Canvas from prompts
AI in Drupal Canvas is taking a leap forward and is already capable of building pages from your prompts! At the Driesnote demo, we saw a prompt to create a landing page about an event. The prompt included the LinkedIn ad copy with the event’s details.
You just enter the prompt into the Drupal Canvas AI, and it is handed behind the scenes to the Orchestration Agent that plans the work and decides which agents should be involved. Most of the work will be done by the Canvas Template Agent. It uses the prompt to decide which component to use, generates content, and searches for relevant images. This agent also has its own access to another agent for a document media search, which can go and verify information you might need from documents like PDFs, in addition to the provided context.
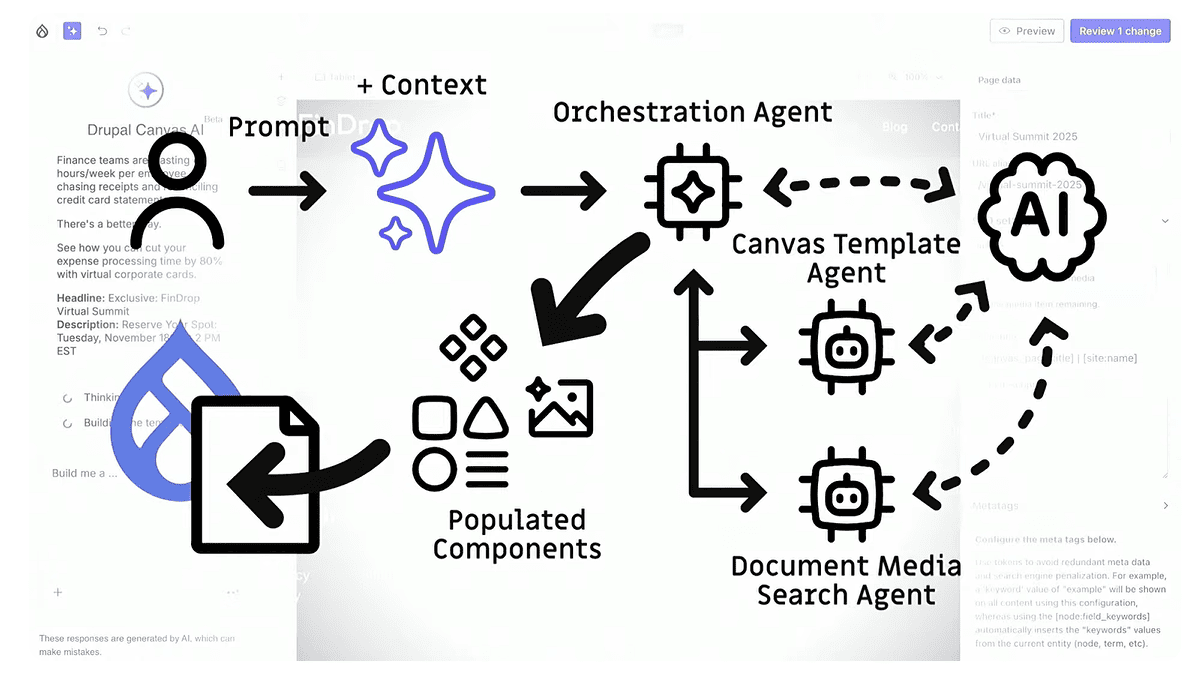
Then Canvas AI is building the layout and populating it with information relevant to our prompt. The result is a fully-structured page that is ready to review, edit, and publish.
As shown in the sidebar, the page is composed of Drupal Canvas components that the AI agents recognized and used. Marketers can use Canvas to edit or fine-tune each part of the page before publishing, and not just the text, but also the layout and components. That’s how Drupal keeps the human in the loop.
That’s how, with some simple instructions, Drupal Canvas uses its own understanding of site structure, media, and component library to assemble an entire page populated with draft content.

Context Control Center: teaching AI your brand voice
To keep every page aligned with your brand voice and key messages, Drupal introduces another powerful feature, the Context Control Center. This is where you define the essentials that guide AI in creating on-brand content: who you are, who you’re targeting, the core facts about your organization, and the messages you want to highlight.

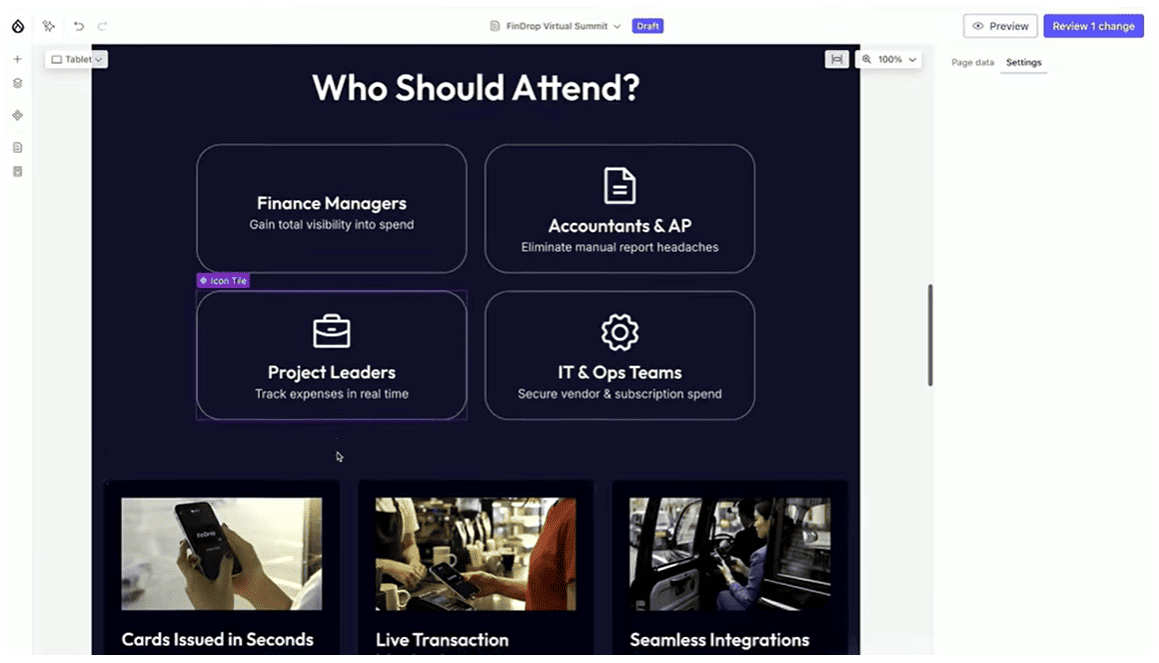
For instance, you can add an Audience Description context in the Control Center and then ask AI to generate a “Who Should Attend” section for an event page. There’s no need to repeat who your target audience is, Drupal AI already understands it from the Context Control Center and will generate a perfectly relevant section automatically.
Intelligence behind the scenes: autonomous Drupal agents
Imagine Drupal AI that doesn’t just wait for your prompt but takes initiative. That’s the idea behind Autonomous Drupal Agents. Of course, all updates still go through a proper review process, keeping humans firmly in the loop.
For instance, when you update key facts or your value proposition in the Context Control Center, the AI automatically refreshes every piece of content that relies on that information. Shortly after, you’ll receive an email notification letting you know that draft updates are ready for review.

Final thoughts
Drupal Canvas marks a bold new chapter for site building. It brings creativity, structure, and intelligence together in one intuitive space, making page creation faster, smarter, and genuinely enjoyable. With each new feature and integration, Canvas moves Drupal closer to its vision of a seamless, modern, and open web experience for everyone.








